

AMRIS transforms AMR and AMU data into evidence for action – protecting human, animal and environmental health in Nigeria
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of today’s most complex health challenges, requiring a coordinated One Health approach across the human, animal and environmental health sectors. Integrated surveillance is essential for understanding how AMR emerges, evolves and spreads across sectors.
AMRIS (Antimicrobial Resistance Information System) is Nigeria’s national platform for AMR and antimicrobial usage (AMU) data. The platform provides a secure, centralised platform for submitting, storing, and analysing AMR and AMU data from hospitals, laboratories, veterinary clinics, pharmaceutical companies, and other contributors, supporting integrated surveillance across the human, animal, and environmental health sectors.
AMRIS enables national and sub-national health authorities, regulators, and healthcare providers to:
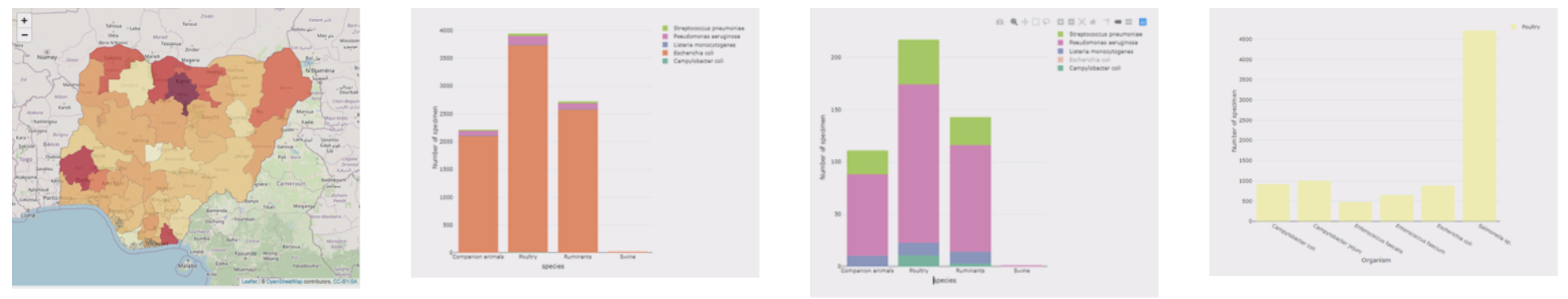
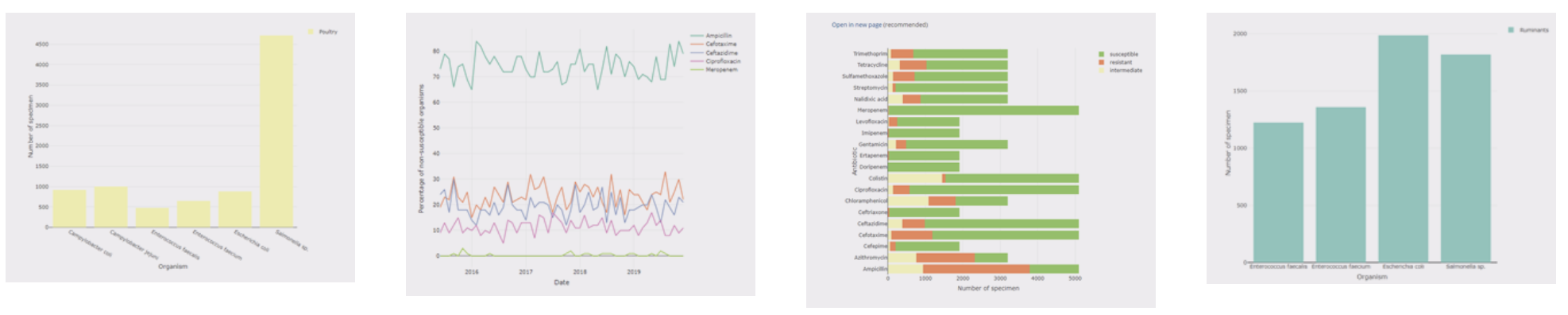
Data submitted to AMRIS is automatically validated and analysed, transforming raw data into usable insights. Users can:
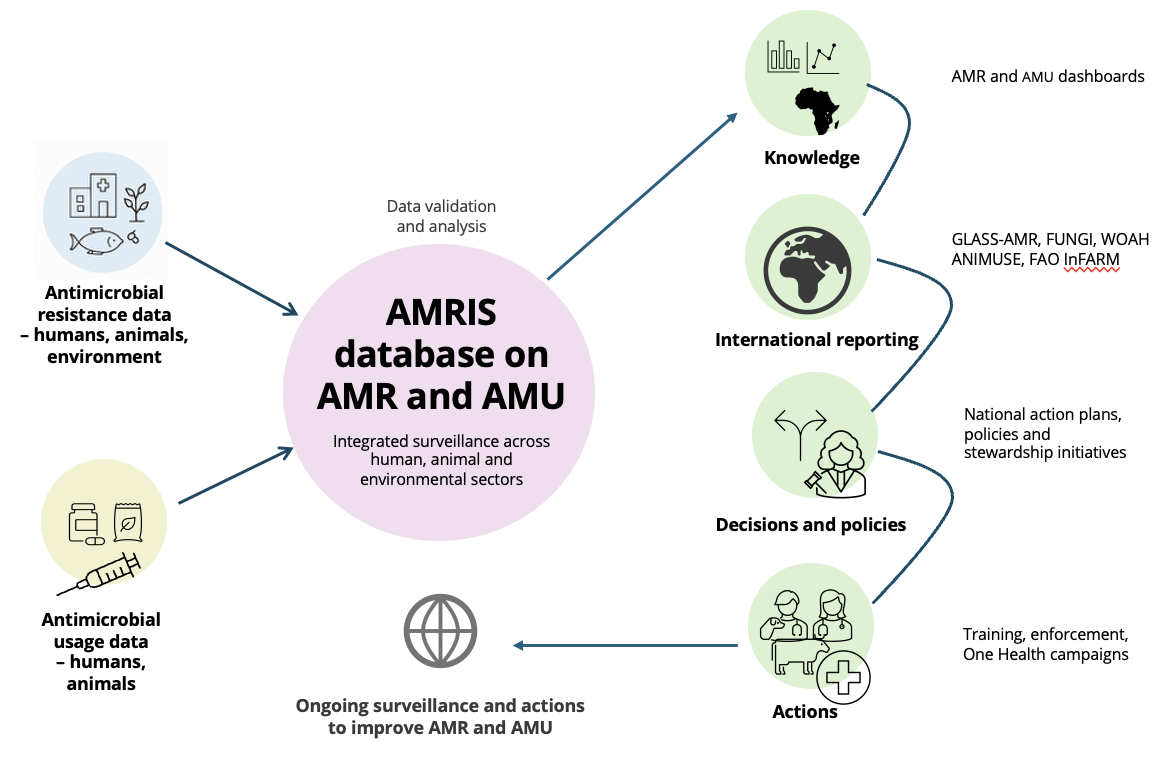
(Diagram adapted from the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH)).
AMRIS was developed in collaboration with the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) and other Federal ministries and technical partners, with support from the UK Government’s Fleming Fund Country Grant to Nigeria.








